42강. 구조체 안에 함수를 집어넣기
// 1시간 = 60분
// 1분 = 60초
// 1시간 = 3600초
// 총 몇초인지 계산 1*3600 + 22 * 60 + 48
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Time {
int h, m, s;
};
int totalSec(Time t) {
return 3600 * t.h + 60 * t.m + t.s;
}
int main() {
Time t = { 1,22,48 };
printf("%d\n", totalSec(t));
}결과 : 4968
int totalSec(Time t){ retrun 3600 * t.h + 60 * t.m + t.s; } 를 구조체 안으로 들여보낼 수도 있다.
괄호 안에 Time t 지우고 t.h 는 h 로 t.m 은 m으로 t.s는 s 로 바꾼다.
printf("%d\n", totalSec(t)); 는 printf("%d\n", t.totalSec()); 으로 바꾼다.
struct Time {
int h, m, s;
int totalSec() {
return 3600 * h + 60 * m + s;
}
};
int main() {
Time t = { 1,22,48 };
printf("%d\n", t.totalSec());
}Time 안에 totalSec라는 함수가 들어간 상태.
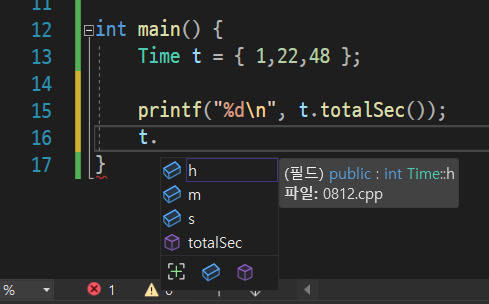
t. 을 타이핑 하면 밑에 h, m , s , totalSec 라는 함수가 나오는데
totalSec 는 Time 이라는 구조체의 하나의 멤버로서 역할을 하게 된다.
그래서 totalSec 멤버 함수 또는 멤버 메소드라고 부른다.
예제) 멤버들의 값을 바꿔보기
struct Point {
int x, y;
void moveRight() { x++; }
void moveLeft() { x--; }
void moveUp() { y++; }
void moveDown() { y--; }
};
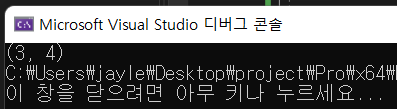
int main() {
Point p = { 2,5 };
p.moveDown();
p.moveRight();
printf("(%d, %d)", p.x, p.y);
}
43강. 구조체 종합문제
1) 다음 프로그램의 출력 결과는?
typedef int Point[2];
typedef Point* PointPtr;
int main() {
Point p = { 3,4 };
PointPtr pp = &p;
printf("%d %d %d\n", **pp, (*pp)[0], (*pp)[1]);
}결과 : 3 3 4
Point p = {3,4}; 의 의미는 int p[2] = {3,4}; 이거랑 똑같다.
PointPtr pp = &p ; 의 의미는 Point *pp =&p; 랑 똑같음
그래서 pp는 p배열을 가리키는 상황
**pp는 *(*pp) 로 쓸수 있다.
*pp 는 p 랑 같으니까 *(*pp) 는 *p 랑 같음
*p = p[0] 이므로 3
(*pp)는 p 랑 같으니까 (*pp)[0] 은 p[0] 과 같다.
그러므로 (*pp)[0]은 3
(*pp)[1] 은 p[1] 이니까 4
2) 빈칸에 들어갈 코드는?
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
void pSwap(Point* p) {
//x좌표와 y좌표를 교환
}
int main() {
Point pos = { 3,4 };
pSwap(&pos);
printf("(%d, %d)", pos.x, pos.y);
}답 :
int tmp = p->x;
p->x = p->y;
p->y = tmp;
struct Point {
int x, y;
};
void pSwap(Point* p) {
int tmp = p->x;
p->x = p->y;
p->y = tmp;
}
int main() {
Point pos = { 3,4 };
pSwap(&pos);
printf("(%d, %d)\n", pos.x, pos.y);
}결과 (4,3)
3) 코드에서 pSwap 함수를 Point 구조체 안에 집어넣기
struct Point {
int x, y;
void pSwap() {
int tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
};
int main() {
Point pos = { 3,4 };
pos.pSwap();
printf("(%d, %d)\n",pos.x, pos.y);
}결과 : ( 4, 3 )
'개발자' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 46~48강 비트연산, 파일 입출력, 유용한 함수들 getchar, putchar, 난수 (0) | 2022.08.12 |
|---|---|
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 44강~45강 상수 만들기 const, 매크로, enum, 매크로 자세히 알아보기 (0) | 2022.08.12 |
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 38 ~ 41강 typedef, 구조체 만들기, 구조체와 메모리, 구조체 가리키기(구조체 포인터) (0) | 2022.08.11 |
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 36강, 37강 배열을 매개변수로 넘기기, 종합문제 (0) | 2022.08.11 |
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 31강~35강 함수, 함수의 반환, call by reference, 프로토 타입, 재귀 함수 (0) | 2022.06.20 |




댓글