46강. 비트연산
1) 비트 논리 연산
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char a = 12, b = 10;
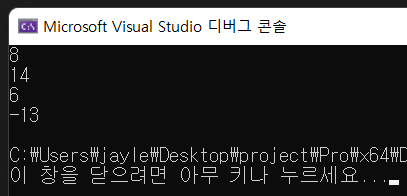
printf("%d\n", a & b);
printf("%d\n", a | b);
printf("%d\n", a ^ b);
printf("%d\n", ~a);
}a=12 이진법으로는 00001100
b=10 이진법으로는 00001010
a&b 는 a && b 해서 00001000 이므로 십진법으로 나타내면 8 이 된다
a| b 는 a || b 해서 00001110 이므로 십진법으로 나타내면 14
a ^ b 는 두개가 다를 때는 1을 반환, 같을땐 0을 반환
00000110 이니까 십진법으로 나타내면 6
-13 을 8비트의 이진수로 나타내면 11110011
a를 완전히 반대로 나타낸것이다.
2) 비트 시프트 연산
시프트(shift) : 옮기다
왼쪽으로 시프트 하는것을 << 오른쪽으로 시프트 하는것을 >>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char a = 22;
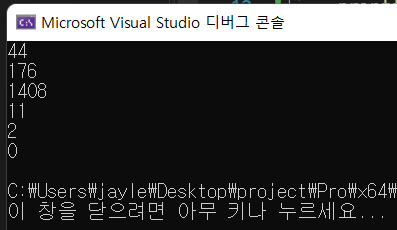
printf("%d\n", a << 1);
printf("%d\n", a << 3);
printf("%d\n", a << 6);
printf("%d\n", a >> 1);
printf("%d\n", a >> 3);
printf("%d\n", a >> 6);
}
char형은 -128 부터 127까지
a<<6 왼쪽으로 시프트를 하면 00010110000000 이 되니까 이게 char 형에서 short 형으로 자동으로 바뀌게 되어 1408이라는 숫자가 나온다.
47강. 파일 입출력
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
FILE* in;
int n;
in = fopen("input12.txt", "r"); //read 의 r
fscanf(in, "%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", n);
}

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
FILE* in, *out;
int n;
in = fopen("input12.txt", "r"); //read 의 r
out = fopen("output12.txt", "w");
fscanf(in, "%d", &n);
fprintf(out, "%d\n", n);
}파일 닫을때는 fclose(in); , fclose(out);
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
FILE* in, *out;
int n;
in = fopen("input12.txt", "r"); //read 의 r
out = fopen("output12.txt", "w");
fscanf(in, "%d", &n);
fprintf(out, "%d\n", n);
fclose(in);
fclose(out);
}int main() {
FILE* in;
int n;
in = fopen("input12.txt", "r"); //read 의 r
printf("in = %d\n", in);
fscanf(in, "%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", n);
fclose(in);
}int main() {
FILE* in;
int n;
in = fopen("input12.txt", "r"); //read 의 r
if (in != nullptr) {
fscanf(in, "%d", &n);
printf("%d\n", n);
fclose(in);
}
}이렇게 if 문 안에 넣으면 파일명이 틀려도 런타임오류가 안난다.
예제 2) 자기 자신 출력하기
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
FILE* in = fopen("081212.cpp", "r");
char ch;
while (!feof(in)) {
fscanf(in, "%c", &ch);
printf("%c", ch);
}
fclose(in);
}
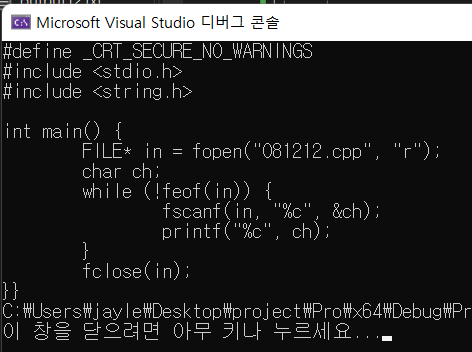
feof 는 end of file 의 약자 파일의 끝을 만나면 true 를 반환
! 붙였으니까 전체의 값이 false 가 되어서 while 문을 빠져나감.
맨 마지막에 중괄호 }} 가 두개
!feof 를 없애고 fscanf를 while 문 안으로 넣을 수 있다.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
FILE* in = fopen("081212.cpp", "r");
char ch;
while (fscanf(in, "%c", &ch) !=EOF) {
printf("%c", ch);
}
fclose(in);
}
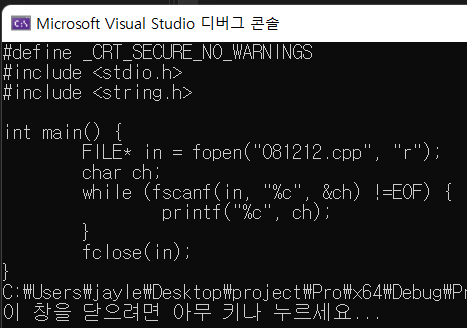
맨 마지막에 중괄호 } 한개임을 확인 할 수 있다.
48강. 입출력과 관련된 유용한 함수들
getchar, putchar
gets, puts (string의 s)
1) getchar, putchar
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char ch;
ch = getchar();
putchar(ch);
}

2) gets, puts
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[100];
gets_s(str);
puts(str);
}

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char str[] = "450";
int n;
sscanf(str, "%d", &n);
printf("n의 값: %d\n", n);
}결과 : n의 값: 450
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
int n = 450;
char str[100];
sprintf(str, "%d", n);
printf("%s\n", str);
}결과 : 450
3) 난수
#include <stdlib.h> 를 추가해야 한다.
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
printf("%d\n", rand());
}
}

1~10 까지의 수 중에 랜덤하게 뽑고 싶다면
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
printf("%d\n", rand()%10 + 1);
}
}

그런데 실행 몇번 해도 계속 똑같은 결과가 나온다.
그래서 seed 를 넣어야 매번 실행할 때마다 값이 바뀌게 된다.
그런데 #include <time.h> 추가 해야됨
time(NULL); 은 1970/01/01 00:00:00 로부터 지난 시간, 초단위
int main() {
printf("%d\n",time(NULL));
}결과

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
srand(time(NULL));
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
printf("%d\n", rand() % 10 + 1);
}
}매번 다른 결과가 나온다.

4) exit(0)
숫자 5개를 입력하고 합을 구하는데 숫자중에 자연수가 아닌 수가 오면 프로그램이 종료되는 프로그램
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n <= 0) {
printf("INPUT ERROR\n");
exit(0);
}
sum += n;
}
printf("%d\n", sum);
}

'개발자' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 개인프로젝트 (0) | 2024.10.20 |
|---|---|
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 44강~45강 상수 만들기 const, 매크로, enum, 매크로 자세히 알아보기 (0) | 2022.08.12 |
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 42~43강 구조체 안에 함수를 집어넣기, 구조체 종합문제 (0) | 2022.08.12 |
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 38 ~ 41강 typedef, 구조체 만들기, 구조체와 메모리, 구조체 가리키기(구조체 포인터) (0) | 2022.08.11 |
| 두들낙서 C/C++ 36강, 37강 배열을 매개변수로 넘기기, 종합문제 (0) | 2022.08.11 |



댓글